Counting VPN packets
There are two ways of counting VPN packets using TMeter. See table below:
| Capturing from NDISWAN interface | Capturing from Ethernet interface | |
| Capturing in promiscuous mode | No (can be counted only the packets with source or destination of your PC) | Yes (can be counted the packets with any source or destination) |
| Counting encrypted VPN packets | Yes | No |
| Type of VPN packets | Any | only which use GRE (number 47) as a transport protocol |
Capturing from NDISWAN interface
This is the simplest way of counting VPN packets. Just select RAS (NDISWANIP) interface for capturing the packets and TMeter will receive "clear" IP packets from your VPN connection(s).
Capturing from Ethernet interface
TMeter can analyze captured VPN packets from an Ethernet interface and count useful information from inside the VPN packet as though it was a regular IP packet. TMeter parses VPN packets, which use GRE (number 47) as a transport protocol. PPP packets (number 0x880B) should be included inside the GRE packets, and also should carry IP packets with any necessary information. VPN packets can be compressed using algorithm MPPC (RFC 2118) but cannot be encrypted.
You should capture VPN packets from any Ethernet interface used for sending/receiving VPN packets. In the this case, TMeter will remove any payload from VPN packet to obtain encapsulated IP packet.
By default, VPN packet analysis is not enabled, but may be enabled in a specific filter by checking the corresponding option in the Filter Editor on the tab "Misc".

VPN packet rules are created exactly as regular IP packet rules because TMeter extracts the IP packet from a VPN packet.
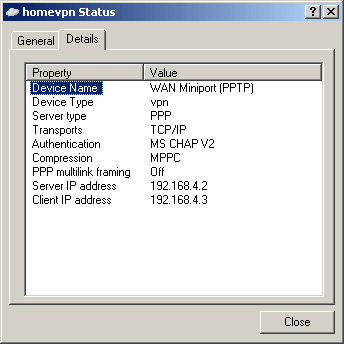
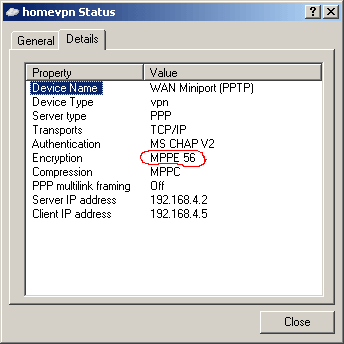
Is my VPN connection encrypted?
Open status window of VPN connection:
|
|
| Status windows without encryption | Status window with encryption |